Gasping for air in the middle of the night can be terrifying. If it happens often, it can lead to fear of falling asleep. But gasping while you sleep is more common than most people think and can be related to sleep-related health conditions such as sleep apnea.
Risk Factors of Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea may affect everyone. Specific factors that can increase the risk of OSA, such as:
Excess weight: Obstructive sleep apnea affects a majority of people who are overweight, although not all. Fat deposits in the upper airway can make breathing difficult.
Older age: Obstructive sleep apnea risk rises with age, although it tends to level out in your 60s and 70s.
Smoking: Smokers are more prone to suffer from obstructive sleep apnea.
A family history of sleep apnea: Having obstructive sleep apnea in your family may raise your risk.
Not Sure Whether You Have Sleep Apnea?
Take a free online Sleep Apnea test if you suspect you may have OSA and want to determine if you are eligible for a home sleep study test.
What Does It Mean When You Gasp for Air?
If you experience gasping for air while you sleep, it means that your breathing has stopped while sleeping. Your body is reacting quickly to resume breathing with a gasping trigger.
What Are the Causes of Gasping for Air?
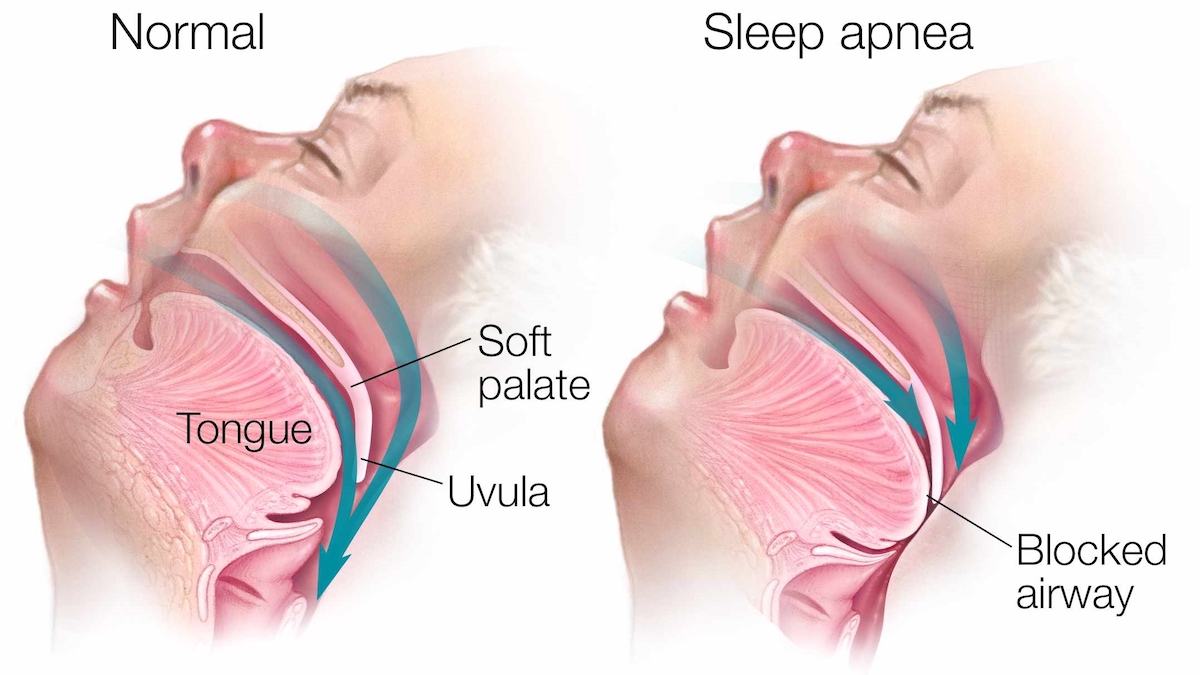
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea can cause the airway to periodically close while asleep causing episodes of gasping at night. Frequent episodes or “apneas” can eventually lead to sleep deprivation.
Postnasal Drip
Postnasal drip causes secretions from the nose that drain down into the throat, causing congestion and cough. It is usually caused by allergies or the common cold and can clog the airway and cause gasping for air.
Nocturnal Asthma
Nocturnal asthma is asthma symptoms when you try to go to bed. This type has symptoms like chest tightness, shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing at night, which can make sleep impossible and leave you feeling tired and irritable during the day.
Anxiety
Anxiety is intense, excessive, and persistent worry and fear about everyday situations. Fast heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, and feeling tired may occur with anxiety which can lead to spasms of gasping.
Acid Reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Acid reflux occurs when the sphincter muscle at the lower end of your esophagus relaxes at the wrong time, allowing stomach acid to back up into your esophagus. This can cause heartburn and gasp for air.
Hypnic Jerk
Hypnic jerks — also called sleep starts — are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions you may experience as you are falling asleep. Some hypnic jerk episodes may cause you to gasp for air.
Pulmonary Edema (Wet Lung)
Pulmonary edema is usually caused by a heart condition and results in fluid in the lungs. Other causes include pneumonia, exposure to certain toxins and drugs, and being at high elevations, which can cause breathlessness.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t pump blood as well as it should. Blood often backs up and causes fluid to build up in the lungs and the legs. The lung fluid buildup can cause shortness of breath.
What Illness Is It When You Gasp for Air Unintentionally?
One of the most common health conditions related to gasping while asleep is sleep apnea. “It is estimated that 22 million Americans suffer from sleep apnea, with 80 percent of the cases of moderate and severe obstructive sleep apnea undiagnosed.”1 Obstructive sleep apnea causes the throat muscles to relax while asleep causing the airway to become closed, which can trigger gasping.
Gasping for Air & Sleep Apnea Therapies
The use of PAP therapy is one of the most effective ways to treat sleep apnea and gasping for air at night. CPAP machines use pressurized air to keep the airway open while you sleep, so respiration remains consistent all night long and you never experience episodes of breathlessness.
Treatments for Waking Up Gasping for Air
Treating The Postnasal Drip
Postnasal drip can be treated with humidified air, staying well-hydrated and sleeping on propped-up pillows.
Treating Hypnagogic Jerks
There are ways to reduce hypnic jerks, including reducing the consumption of stimulants such as nicotine or caffeine, avoiding physical exertion before sleep, and consuming sufficient magnesium. Some medications can also help to reduce or eliminate the hypnic jerks.
Treating Anxiety and Panic Disorders
Psychotherapy is considered an effective first-choice treatment for panic attacks and panic disorder. Psychotherapy can help you understand panic attacks and panic disorders and learn how to cope with them.
Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea can be treated with CPAP therapy which uses a CPAP machine to flow pressurized air into the airway to prevent the airway from closing at night.
Treating Pulmonary Edema
Lifestyle changes can help reduce the symptoms of pulmonary edema including maintaining healthy blood pressure, reducing salt intake, and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea Through a Home Sleep Apnea Test
If you are experiencing gasping while you sleep, you may have obstructive sleep apnea. The first step in knowing for sure is to get an accurate diagnosis.
You can receive a diagnosis in the comfort of your bed with Sleep Care Online. Here is how it works.
- With the Complete Care Package, schedule a 10-minute telehealth visit with a healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms, upcoming sleep study, test results, and treatment options.
- A multi-night, disposable home sleep apnea test is mailed to your home to be completed at your convenience.
- A physician analyzes the sleep data and provides a prescription if needed.
- Schedule an optional follow-up appointment (additional fee applies).
- We connect you to sleep experts who can offer customized sleep therapy options, assistance in equipment purchase, and initial set-up.
Reference:
1.Sleepapnea.org. Sleep Apnea Information for Clinicians. Accessed April 2021.